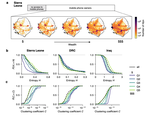
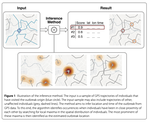
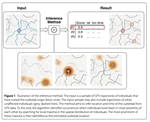
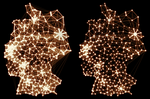
human mobility
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 117 (52), 32883-32890
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic many countries implemented containment measures toreduce disease transmission. Studies using digital data sources …
Bunde A., Caro J., Kärger J., Vogl G. (eds) Diffusive Spreading in Nature, Technology and Society. Springer, Cham.
Disease dynamics is a complex phenomenon and in order to address these questions expertises from many disciplines need to be integrated. One method …